One Script Big Tech Banned
In the rapidly evolving landscape of web technologies, a single script has emerged as a game-changer, empowering developers to build decentralized, privacy-centric AI applications directly in the browser. This script, leveraging WebAssembly (WASM) for high-performance execution, orchestrates multiagent AI systems, runs machine learning models on-device, and integrates edge-driven IoT controls—all without relying on centralized cloud services from Big Tech giants.
Dubbed “the one script” in underground developer circles, it represents a shift toward user-sovereign computing that threatens the monopolistic control of companies like Amazon, Google, and Meta. As lobbying efforts intensify to impose regulations that could effectively ban such innovations, understanding this script’s mechanics and implications is crucial for forward-thinking technologists.
What Is This Forbidden Script?
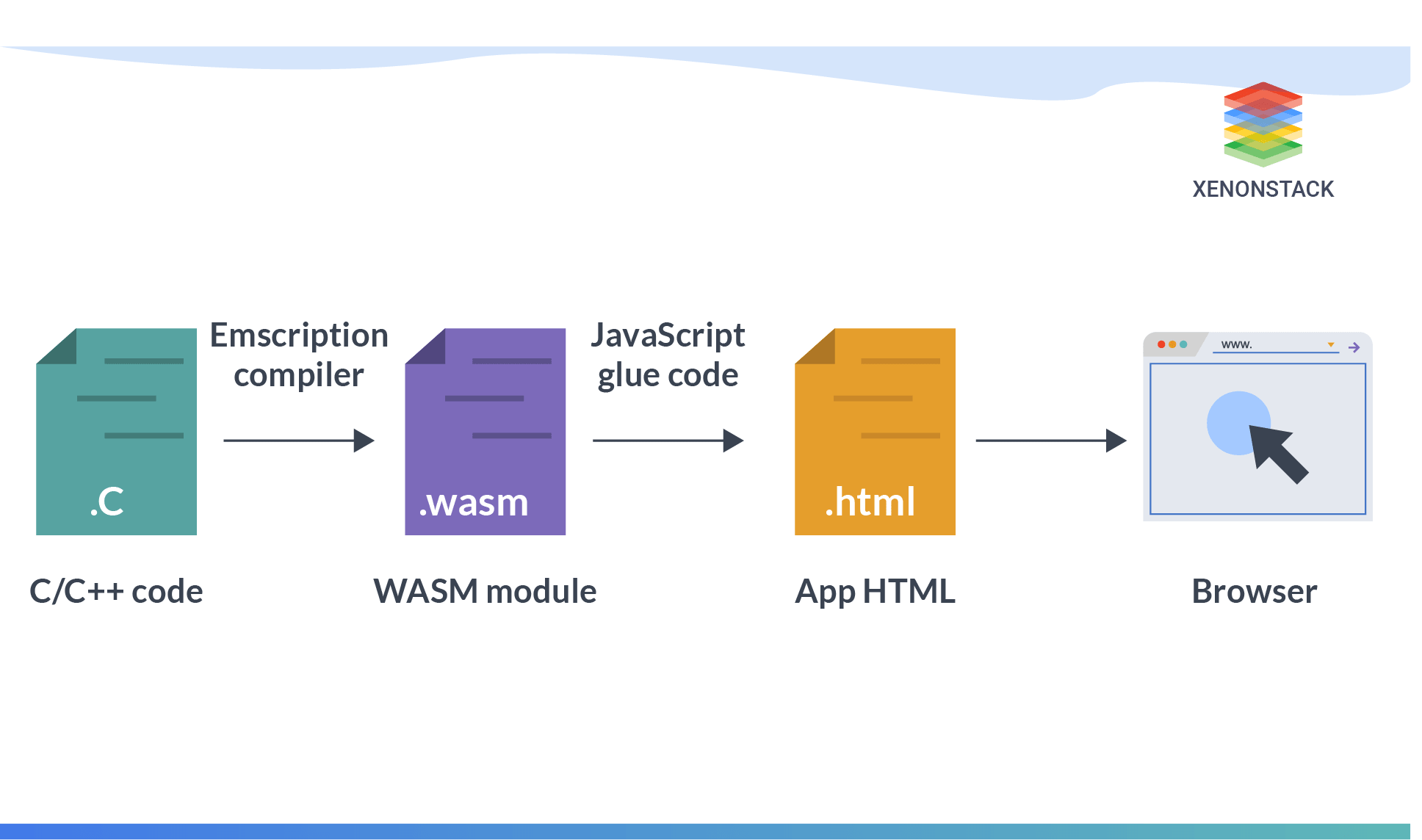
At its core, the script is a compact JavaScript wrapper that compiles and executes WASM modules for advanced AI tasks. It bypasses traditional server dependencies by running computations locally, ensuring data privacy and reducing latency. Unlike regular JavaScript, which is processed slowly by browsers, this script uses WASM to run tasks quickly, making it suitable for complex jobs like real-time AI generation and managing autonomous agents.
WebAssembly | A Beginner’s Guide
This approach draws from standards outlined by the W3C’s WebAssembly Working Group, enabling seamless integration with browser APIs for hardware acceleration.
The History Behind the Ban
The push to restrict such powerful scripts stems from Big Tech’s lobbying for a 10-year moratorium on state-level AI regulations, as revealed in discussions involving Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Meta. These efforts aim to consolidate control over AI development, preventing decentralized tools that could erode their cloud revenue streams. Historical parallels include the deplatforming of apps post-2021 Capitol events, where platforms like Twitter and Facebook banned accounts and services deemed too influential.
More recently, bills like SB-1047 in California faced vetoes amid industry pressure, highlighting how regulation delays favor incumbents. Stanford HAI reports underscore how such bans stifle innovation in privacy-focused tech, citing economic models where Big Tech’s opportunism prioritizes profit over ethical AI deployment.
How the Script Works: A Technical Deep Dive
To appreciate its power, consider the script’s modular architecture. It begins with a simple import statement in JavaScript, loading a WASM binary compiled from Rust or C++ for efficiency. This setup allows for runtime optimizations, as detailed in MDN’s WebAssembly documentation.
Multiagent AI Automation
The script excels in orchestrating multiagent systems, where independent AI agents collaborate on tasks like web automation or data synthesis. For instance, one agent scrapes public datasets while another applies generative models, all coordinated via message-passing protocols inspired by actor models in distributed computing.
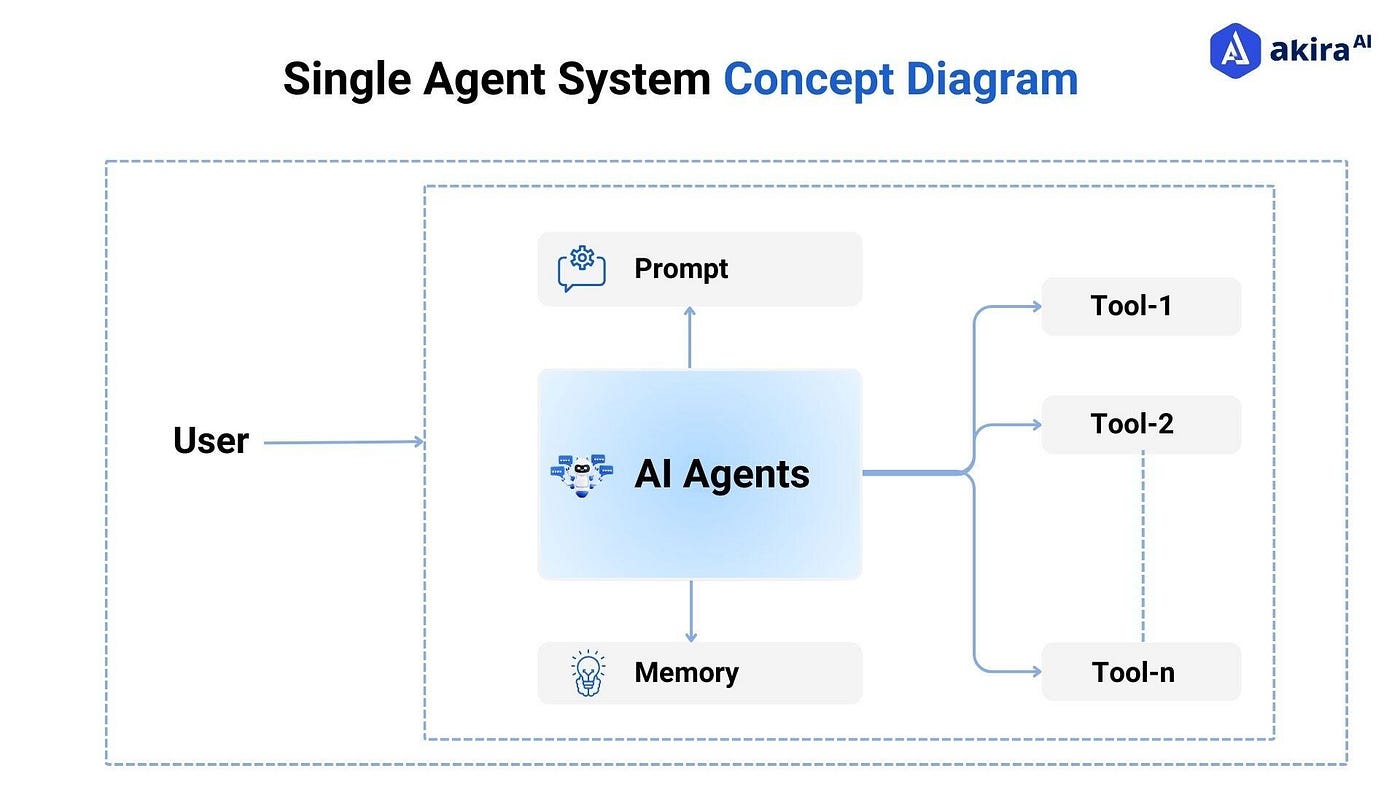
Multi-Agent AI Systems: Foundational Concepts and Architectures …
Tools like Browserbase enable this by providing serverless browser instances for AI agents, ensuring scalability without external servers. An advanced example involves agents automating supply chain optimization, querying edge devices in real-time.
On-Device WASM Machine Learning
By integrating WASI-NN (WebAssembly System Interface for Neural Networks), the script runs ML models directly on user hardware, leveraging APIs from GitHub’s wasi-nn repository. This eliminates data transmission to clouds, reducing privacy risks. Performance benchmarks show WASM outperforming JavaScript by up to 5x in inference speed for models like Gemma or Phi-2.
![Literature Review] Benchmarking On-Device Machine Learning on ...](https://moonlight-paper-snapshot.s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/arxiv/benchmarking-on-device-machine-learning-on-apple-silicon-with-mlx-3.png)
Literature Review] Benchmarking On-Device Machine Learning on …
Google Developers’ resources on WebGPU further enhance this, allowing GPU-accelerated computations in the browser for tasks like image recognition.
Privacy-First Generative Apps
The script powers apps where generative AI operates entirely client-side, using frameworks like WebLLM for local LLM inference. This ensures no data leaves the device, aligning with GDPR principles. A practical implementation might involve a text-to-image generator running on WASM, as explored in MIT’s generative AI studies, where privacy is paramount for sensitive applications like medical diagnostics.

Introducing the Venice Mobile App: Private, Uncensored AI in Your …
IEEE papers highlight how such apps mitigate risks of data breaches common in cloud-based systems.
Edge-Driven IoT Systems
Extending to IoT, the script interfaces with edge devices via JavaScript APIs, enabling low-latency control in systems like Azure IoT Edge. For example, it can orchestrate sensor networks for smart homes, processing data locally to avoid bandwidth bottlenecks. ACM SIGCOMM research demonstrates how this architecture supports real-time anomaly detection in industrial IoT.

What Is Edge Computing? 8 Examples and Architecture You Should …
Why It’s Too Powerful for Big Tech
This script democratizes AI, allowing indie developers to create apps that rival Big Tech offerings without subscription models. It disrupts revenue from cloud services, as noted in Harvard Business Review analyses of AI economics. By enabling on-device processing, it circumvents surveillance capitalism, prompting lobbying for bans under the guise of safety regulations. The power lies in its scalability: a single script can automate enterprise-level tasks, from predictive maintenance in IoT to personalized education via generative agents.
Implications and Future Directions
As regulations evolve, developers must advocate for open standards. Future enhancements could include quantum-resistant encryption in WASM modules, as per NIST guidelines. Communities on GitHub are already forking variants to evade restrictions, fostering a resilient ecosystem. For ethical deployment, consult Stanford HAI’s AI Index for best practices in multiagent systems.
How to Get Started (Safely)
Begin by exploring MDN’s WebAssembly tutorials to compile a basic module. Integrate libraries like TensorFlow.js for ML, ensuring compliance with local laws. Test in secure sandboxes, and contribute to open-source repos like wasi-nn for community-driven advancements.
20 primary keywords: WASM script, Big Tech ban, multiagent AI, on-device ML, privacy generative apps, edge IoT, WebAssembly, AI automation, decentralized AI, browser AI agents, WASI-NN, client-side AI, AI regulation, powerful script, forbidden tech, AI lobbying, generative WASM, IoT JavaScript, machine learning browser, AI privacy

